What is Urinary Tract Infection? Symptoms and Causes
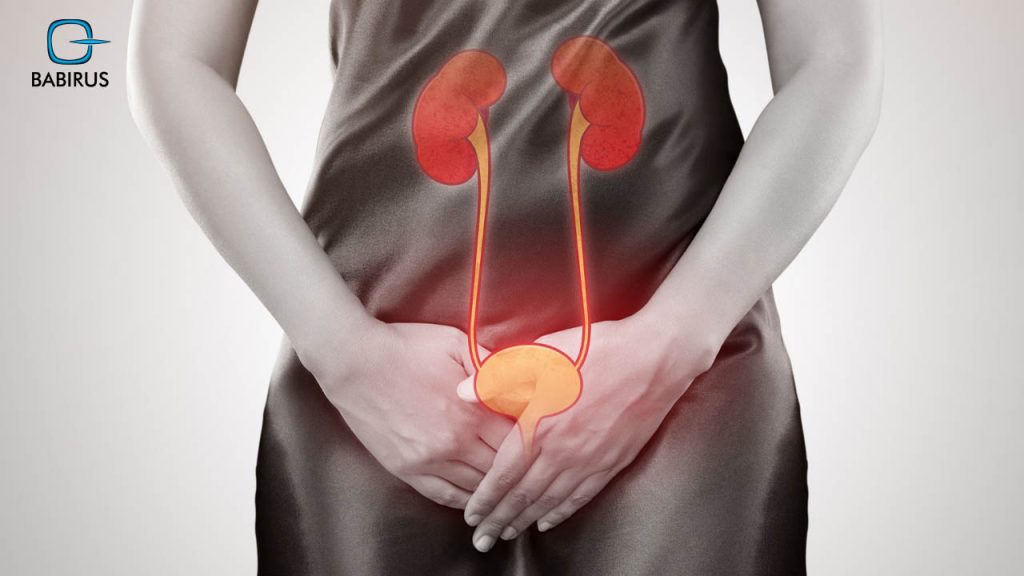
About 60% of women and 12% of men will suffer from urinary tract infection (UTI) at least once in their lifetime, thus, you can estimate how common this condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments for UTIs, as well as some prevention strategies to help you avoid getting a UTI in the first place.
What Is Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract and cause inflammation, leading to symptoms such as burning during urination, frequent urination, and abdominal pain.
Moreover, it may include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, more than that, although UTIs can affect anyone, but they are most common in women and children.
Exploring the 5 Different Types of UTIs
There are several types of urinary tract infections (UTIs) based on the location of the infection within the urinary system.
Although, these types of UTIs can vary in severity, yet, they all require appropriate diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications and recurrence.
1. Understanding Cystitis: Symptoms and Treatment
The most common type of UTIs that inflect the bladder.
Symptoms of Cystitis: may include frequent and painful urination, blood in the urine, and pelvic discomfort.
2. Pyelonephritis: Causes, Complications, and Treatments
Pyelonephritis is a UTI that affects the kidneys, and it is considered a kind of dangerous UTI that could cause different complications such as kidney damage if not probably treated.
Symptoms of Pyelonephritis: could contain fever, chills, back or side pain, nausea, and vomiting.
3. Urethritis: Symptoms and Management
Urethritis refers to the inflammation of the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Symptoms of Urethritis: such as burning or pain during urination and an increased urge to urinate.
4. Prostatitis: UTI in Men
Prostatitis is a UTI that affects the prostate gland in men.
Symptoms of Prostatitis: such as pain in the groin, pelvic area, or lower back, as well as difficulty urinating.
5. Asymptomatic Bacteriuria: A Silent UTI
This type of UTI does not cause any noticeable symptoms but involves the presence of bacteria in the urine, and it is often detected through urine tests conducted for other medical reasons.
Understanding the Causes of UTIs
As we said, the urinary tract infection is caused by bacteria that enter the urinary tract and cause inflammation, and the most common bacteria that cause UTIs are Escherichia coli (E. coli), Klebsiella, and Staphylococcus.
Moreover, the urinate tract infection can occur when:
- Bacteria from the skin or rectal area enter the urinary tract through the urethra.
- Bacteria from an earlier infection in the urinary tract that did not fully heal, leading to a recurrent infection
- A problem with the urinary tract, such as a stone or blockage, that prevents proper urine flow and allows bacteria to grow.
- The immune system is weakened, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections.
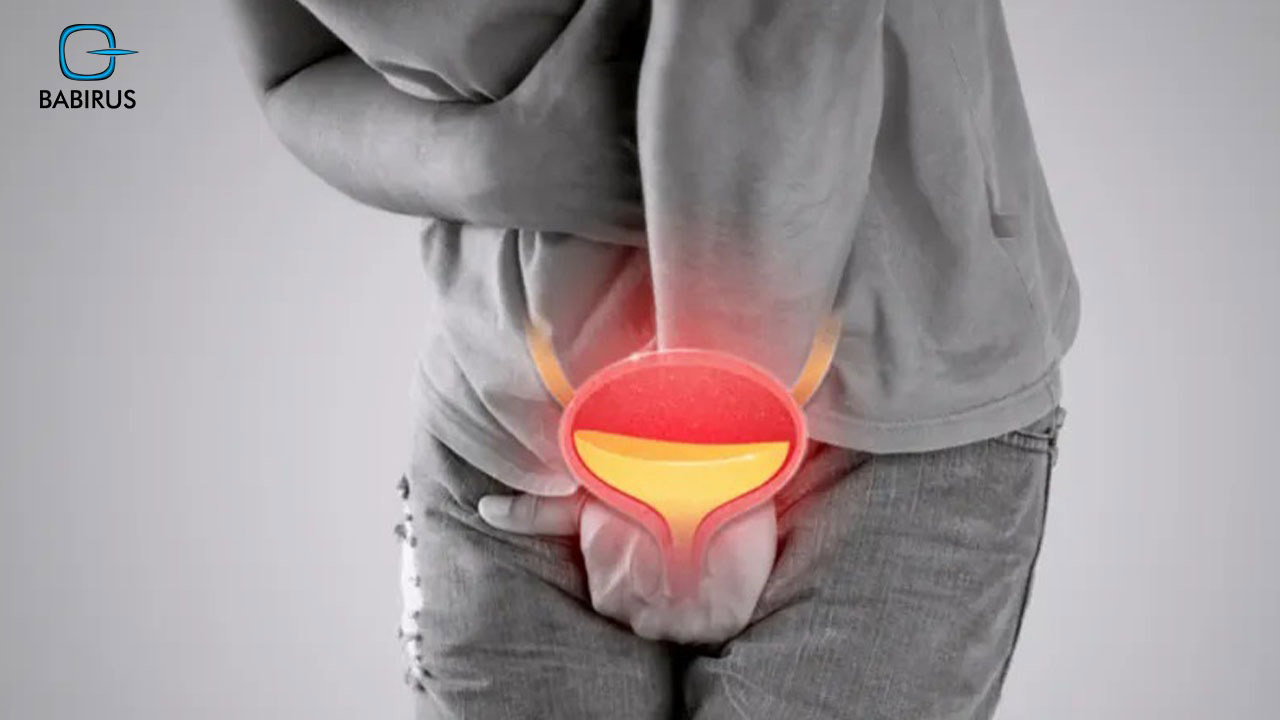
Recognizing Common UTI Symptoms
The symptoms of UTI can vary depending on the location of the infection, but common symptoms include:
Lower UTI (bladder infection):
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate.
- A burning sensation while urinating.
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Fever and chills.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Upper UTI (kidney infection):
- Severe pain in the side or back.
- Fever and chills.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Frequent urination.
- Blood in the urine.
Treating Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infection treatment relies mostly on antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
However, the choice of antibiotic and duration of treatment depends on the severity and location of the infection, as well as the patient’s medical history and any underlying health conditions.
Moreover, most treatment strategies include these stages:
- Taking antibiotics, like trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, fosfomycin, and ciprofloxacin.
- The duration of antibiotic treatment for UTIs can vary depending on different factors and usually ranges from 3 to 7 days.
- Pain management may be recommended to alleviate discomfort associated with UTIs with over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Increasing fluid intake, particularly water, is often recommended as part of UTI treatment.
- After completing a course of antibiotics, individuals with UTIs need to follow up with their healthcare provider to ensure that the infection has been effectively treated.
- Follow preventive measures to reduce the risk of recurrent UTIs.
Managing UTIs: Do’s and Don’ts
There are some basic recommendations for what you should or should not do while suffering from a urinary tract infection:
The DOs in Managing UTIs:
- Drink 6 to 8 glasses of water daily, as drinking water and cranberry juice may help the treatment of UTIs.
- Follow good hygiene practices. Women should wipe from front to back after using the toilet. Avoid douches and sprays (increase chances of getting UTIs). Showers may be better than baths. Wear cotton underwear and avoid tight pants.
- Try to urinate often and empty your bladder completely.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you take birth control pills as some antibiotics interfere with birth control pills.
- Take antibiotics until they are gone, especially if you get UTIs often, your healthcare provider may give you antibiotics to prevent them.
- Call your healthcare provider if your fever continues after 48 hours of antibiotic therapy or if symptoms return after you finish your antibiotics.
The DON’Ts in Managing UTIs:
- Skip doses or stop taking antibiotics before they are gone.
- Have sex until the fever and symptoms stop.
- Hold your urine for long periods.
- Drink caffeinated beverages or alcohol.
Additional Tips for UTI Prevention
The urinary tract infection is a common and undangerous infection, yet it requires following up the treatment, and continuous care of your hygiene.
However, avoid the bad impacts of this infection with the right treatment and procedures, and do not hesitate to contact us for any medical help or advice.
