All About TB (Tuberculosis) Test
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs and could spread causing serious complications, thus, the diagnosis of TB with a reliable tuberculosis test is more than essential in the fight against TB.
The tuberculosis test is the first step in effectively diagnosing and treating tuberculosis before it becomes a life-threatening situation.
Today, we are going to share with you full information on tuberculosis tests, with types, attached risks, and the process of tuberculosis tests.
What Is a TB (Tuberculosis) Test?
A tuberculosis test is a diagnostic test that is used to determine whether a person has been infected with the bacteria Mycobacterium Tuberculosis or not.
However, keep in mind that a positive result indicates that the person has been infected with the TB bacteria at some point, but it does not necessarily mean he/she have active tuberculosis. Thus, further tests will be required to confirm the diagnosis, such as chest X-rays and sputum tests,
Who Should Be Screened For TB?
Screening for TB is essential to identify and treat the infection in the best way, moreover, prevent its spread. The following groups of individuals are high-risk populations that should be screened for TB:
- Individuals with known exposure to TB patients.
- People living with HIV/AIDS.
- Healthcare workers who work in high-risk settings.
- Residents and employees of congregate settings such as prisons and homeless shelters.
- Immunosuppressed individuals, including those receiving immunosuppressive therapy or organ transplant recipients.
Who Performs a TB Test?
The decision of who can perform the tuberculosis test varies depending on the healthcare setting and the local regulations governing medical procedures, however, in most cases, TB tests are conducted by authorized healthcare providers in healthcare facilities.
Healthcare Professionals:
- Doctors
- Nurses
- Medical Technicians.
TB Testing Facilities:
- Hospitals.
- Clinics
- Public health departments.
- Community health centers.
- Occupational health facilities.
- Correctional institutions.
- Military healthcare facilities.
Types of Tuberculosis Test:
The choice between different types often depends on factors such as the individual’s situation including the medical history, age, and other considerations, to decide which tuberculosis test is most appropriate for your situation.
Both types of tuberculosis tests are used to identify individuals who may have been exposed to tuberculosis and who may require further evaluation or treatment, meaning that they are not diagnostic for active tuberculosis but rather indicate whether an individual has been infected with the bacteria or not.
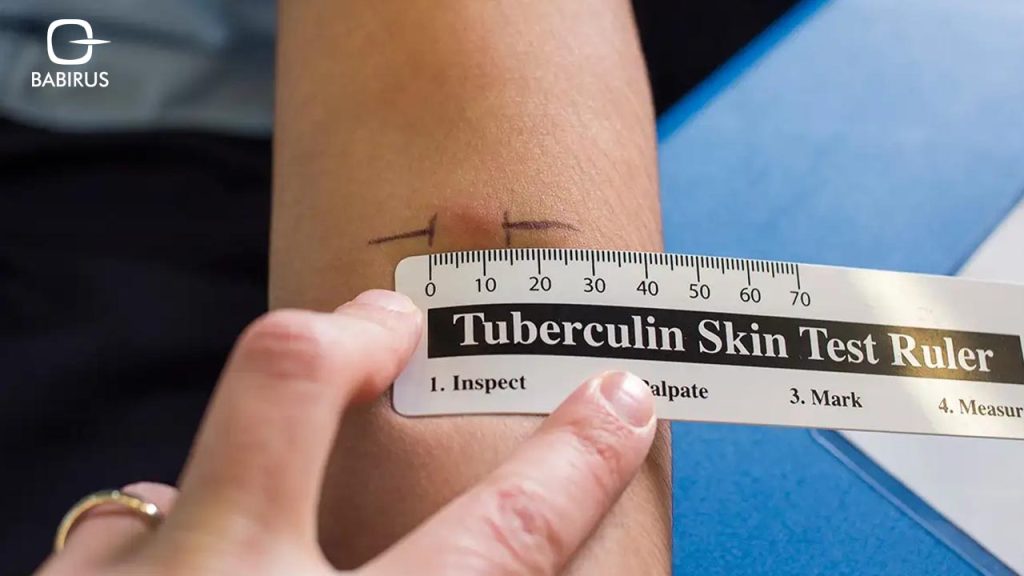
· Tuberculin Skin Test (TST):
The tuberculin skin test, also known as the Mantoux test, includes injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin into the skin of the forearm.
And then after 48 to 72 hours, a healthcare professional checks the injection site for a raised, hardened area called an induration, the size of the induration is measured to determine if the test is positive or negative.
Additionally, a positive TST result shows that the person has been infected with the tuberculosis bacteria at some point in his/her life. However, it does not necessarily mean that they have active tuberculosis. Then, as we said earlier, further evaluation may be needed to confirm the current presence of active tuberculosis.
· Tuberculosis Blood Test (IGRA):
The TB blood test, or interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA), measures how a person’s immune system reacts to the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, by detecting the release of interferon-gamma when whole blood is exposed to specific TB antigens.
This tuberculosis test is often used as an alternative to the TST, especially for individuals who have received the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine or who have difficulty returning for a second appointment to have their TST result read.
How Does a TB (Tuberculosis) Test Work?
Both types of TB tests work by measuring your immune system’s response to antigens taken from the bacterium that causes TB.
· How Does a TB Skin Test Work?
A TB skin test measures your immune system’s response to a purified protein derivative (PPD) solution injected under your skin. PPD is a protein that comes from the bacteria that causes TB.
Note that it is not live bacteria, and it will not make you sick, however, if you have ever been exposed to the TB bacteria, your skin will react to the antigens by developing a firm, red bump at the site of the injection within three days.
· How Does a TB Blood Test Work?
In most cases, if you have been infected with TB, blood cells from your blood sample will release a protein called interferon-gamma (IFN- γ) when mixed with antigens derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a laboratory.
To conduct the tests, laboratory scientists mix your blood sample with antigens and controls and measure the reaction using a method called immunoassay, moreover, they will share your results as negative, positive, or indeterminate.
What Are the Risks of a TB (Tuberculosis) Test?
The tuberculin skin test, also known as the Mantoux test, is a common method used to detect tuberculosis (TB) infection. While the test is generally safe, there are potential risks associated with it.
- Pain and discomfort at the injection site, with redness, swelling, or tenderness usually subsiding within a few days.
- False positive results may occur in individuals vaccinated with BCG or exposed to non-tuberculosis mycobacteria, leading to unnecessary follow-up tests and treatment.
- Positive TB test results can cause significant anxiety and stress, especially in asymptomatic individuals with no known exposure to TB.
- In rare cases, severe allergic reactions to the tuberculin solution may occur, with symptoms like hives, difficulty breathing, and swelling.
- While uncommon, there is a risk of infection at the injection site following a TB test, minimized with proper sterilization and care.
- Fainting or light-headedness may occur due to fear or anxiety related to needles or medical procedures during or after the test.
Type of TB (Tuberculosis) Test Results:
The results of a tuberculosis test could be either negative or positive, as it only shows if you have been exposed to the TB (tuberculosis) infection or not.
· Positive Tuberculosis Test:
If your tuberculosis test is positive, it likely means you have been exposed to the bacterium that causes TB.
Then, your healthcare provider will likely request more tests to help make a confirmed diagnosis, including chest X-rays and laboratory tests on a sputum sample to set the appropriate treatment for your TB condition, whether it is latent or active.
· Negative Tuberculosis Test:
If your tuberculosis test is negative, you likely have not been exposed to the TB bacterium. A negative TB skin test means your skin did not react to the liquid.
However, if your test is negative but you have symptoms of TB, you may need further testing.
3 Most Common Questions Tuberculosis:
Find professional answers from our professionals to the FAQs of tuberculosis:
Can TB Be Cured?
Yes, Tuberculosis (TB) can be cured with a combination of antibiotics taken over a specific period, typically six to nine months with medical supervision.
Moreover, it is crucial for individuals with TB to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by a healthcare professional to ensure the complete eradication of the bacteria and prevent the development of drug-resistant strains.
How Do You Know If Your TB Is Positive?
If you suspect that you may have contracted TB, it is vital to recognize the symptoms and consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The most common symptoms of TB infection include:
- Persistent coughing that lasts for more than two weeks or coughing up blood.
- Chest pain and difficulty breathing.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Fever and night sweats.
- Chills and loss of appetite.
How Long Do Tuberculosis Tests Take?
The Tuberculin Skin Test takes 48 to 72 hours, while the Interferon Gamma Release Assay takes approximately 24 hours to yield results, remember that it is vital to consult with a healthcare provider to determine which type of TB test is most appropriate for you.
TB (tuberculosis) Test in UAE,
TB is a significant global health issue, and early detection through testing is crucial for effective treatment and control of its spread. In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), TB testing and treatment are available through both public and private healthcare providers.
Contact us immediately to guide you with the best diagnostics solutions.