The Importance of Sterilization in Surgical Instrumentation
Sterilization is a vital procedure in healthcare facilities to prevent the spread of infections and ensure patient safety. Thus, proper sterilization in surgical instrumentation is required to maintain a clean and sterile working environment.
As even the most successful surgery or procedure will become a disaster if sterilization in surgical instrumentation is not done effectively.
In this article, we will explore the sterilization of surgical instrumentation process, moreover, focus on the sterilization process types, included steps, and the several available techniques and equipment commonly used in medical sterilization settings.
What Is Surgical Instrumentation?
Surgical instrumentation term is used to refer to all the tools and devices used by medical professionals during surgical procedures.
Moreover, these instruments are what make the work more efficient and even possible, as they help doctors perform various tasks, such as cutting, grasping, holding, retracting, clamping, or suturing tissues.
However, the quality and precision of surgical instruments significantly impact the success of a surgical procedure, patient safety, and postoperative recovery.
The Main Types of Surgical Instrumentation:
There are many types of surgical instruments, classified based on their function or the specific surgical procedure they are used for. Some common categories include:
– Cutting Instruments:
Scalpels, scissors, and surgical blades are examples of cutting instruments used to incise tissues or remove lesions.
– Grasping and Holding Instruments:
Forceps and hemostats are designed to hold, grasp, or clamp tissues to control bleeding or manipulate organs during surgery.
– Retracting Instruments:
Retractors are used to hold open an incision or organ to provide better visibility and access to the surgical site.
– Clamping Instruments:
Clamps are employed to control bleeding by applying pressure on blood vessels or holding together tissue edges.
– Suturing Instruments:
Needle holders and suture materials are used to resemble tissue edges and facilitate wound healing.
What Is Sterilization in Surgical Instrumentation?
Sterilization in surgical instrumentation is the used expression to talk about the process of removing all forms and types of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, from the surfaces of surgical instruments.
This process is essential in preventing the transmission of infectious factors between patients and reducing the risk of postoperative complications.
4 Included Steps in the Sterilization Process:
If you want to go through an effective sterilization in the surgical instrumentation process, then you must accurately follow these 4 steps:
1. Cleaning:
Before starting the sterilization, surgical instruments must undergo thorough a cleaning step to remove any visible debris, blood, or tissue. This step is vital for active sterilization as the existence of organic material can interfere with the process.
2. Sterilization Methods:
There are several methods of sterilizing surgical instruments, including:
- Steam sterilization (autoclaving).
- Ethylene oxide gas sterilization.
- Hydrogen peroxide gas plasma sterilization.
- Chemical sterilant.
Although each method has its advantages and limitations, however, you should choose the best sterilization method depending on the type of instrument and material.
3. Validation and Monitoring:
It is crucial to validate the effectiveness degree of the sterilization process through routine monitoring and testing.
This could be done by using biological indicators to ensure that the sterilization equipment is functioning correctly and achieving the desired level of sterility.
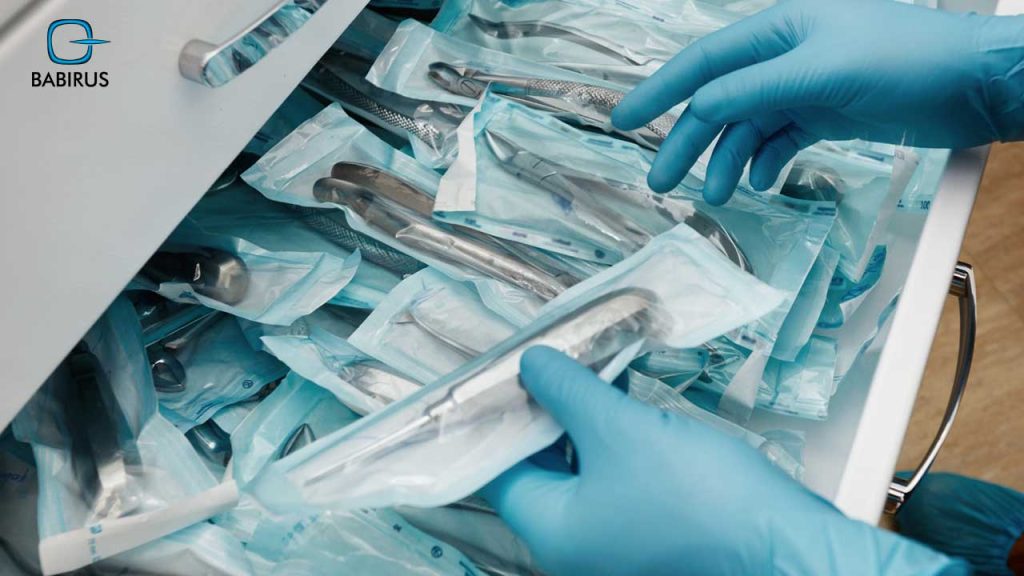
4. Storage and Handling:
Once the surgical instruments are 100% sterilized, they must be stored in a clean and dry environment to maintain their sterility.
More than that, the proper handling practices, such as using sterile drapes or pouches, help prevent any contamination before use.
The Importance of Sterilization in Surgical Instrumentation:
Sterilization in surgical instrumentation is crucial for several reasons:
- The sterilization process helps prevent surgical site infections (SSIs)by ensuring that instruments are free from pathogens that could cause postoperative complications. SSIs can lead to prolonged hospital stays, increased healthcare costs, and even mortality in severe cases.
- The proper sterilization of surgical instruments protects both patients and healthcare workers from exposure to infectious agents. Thus, by following strict sterilization protocols, healthcare facilities can ensure a safe environment for all individuals involved in surgical procedures.
- Sterilization ensures the longevity and effectiveness of surgical instruments. As contaminated or improperly sterilized instruments can become damaged over time, leading to potential malfunctions during surgery. This means that regular sterilization practices help extend the lifespan of instruments and maintain their quality for repeated use.
Sterilization Techniques and Equipment:
Today, with all the technical advancement there are many effective sterilization techniques, that are used for sterilizing surgical instruments, each with its unique advantages and applications.
Common Sterilization Techniques:
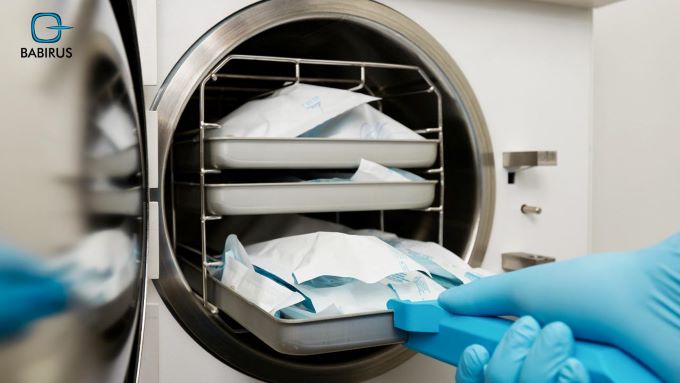
– Autoclaving:
Autoclaving is one of the most widely used methods of sterilization in healthcare settings. It involves using steam under pressure to kill microorganisms on heat-resistant materials such as surgical instruments, glassware, and medical waste.
Autoclaves are highly effective at achieving sterilization and are relatively easy to use.
– Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Sterilization:
Ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization is usually used for heat-sensitive medical devices that cannot withstand high temperatures. EtO gas can enter packaging materials to kill microorganisms without causing damage to the items being sterilized.
However, although this method is efficient for an extensive range of medical devices, yet it requires appropriate ventilation due to the toxic nature of EtO gas.
– Chemical Sterilant:
Chemical sterilants such as hydrogen peroxide, peracetic acid, and glutaraldehyde are used to sterilize heat-sensitive medical devices and equipment.
These chemicals work by disrupting the microorganisms’ cell structure, and effectively killing them. Chemical sterilants are usually used for endoscopes, respiratory therapy equipment, and other delicate instruments.
– Radiation Sterilization:
Radiation sterilization methods, including gamma irradiation and electron beam irradiation, use high-energy radiation to kill microorganisms on medical devices and supplies.
Keep in mind that these methods are effective for single-use disposable items and products that cannot be autoclaved or treated with chemicals.
Sterilization Equipment:
– Autoclaves:
Autoclaves are essential pieces of equipment in healthcare facilities for steam sterilization. They come in various sizes and designs to accommodate different types of instruments and materials.
Moreover, modern autoclaves offer advanced features such as programmable cycles, temperature monitoring, and drying functions.
– Sterile Processing Systems:
Sterile processing systems include washers, disinfectors, sterilizers, and storage solutions that work together to ensure the cleanliness and sterility of medical instruments and equipment.
These systems are designed to streamline the sterilization process while maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
– Biological Indicators:
Biological indicators are the used tools to monitor the effectiveness of sterilization processes by containing harmless bacterial spores that are more resistant than typical pathogens. These indicators are placed inside autoclaves or other sterilization equipment during each cycle to verify that the desired level of sterility has been achieved.
Last but not least,
Sterilization in surgical instrumentation is a critical aspect of healthcare that ensures patient safety and reduces the risk of infections. The importance of sterilization cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in maintaining the hygiene and safety of patients, medical staff, and the healthcare environment.
Thus, ensuring proper sterilization techniques and the use of appropriate sterilization methods are essential to minimize the risk of infections and improve patient outcomes.