Cytopathology and Respiratory Diseases
Cytopathology plays a great role in dealing with and treating respiratory diseases that are a real concern around the world, thus, we can say that cytopathology and respiratory diseases have a great attachment in treatment strategy and make treatment numbers better.
Moreover, cytopathology is considered one of the best tools in diagnosing, understanding, and addressing respiratory health issues, due to its advanced capability in examining cells to uncover what is happening inside the respiratory system.
Thus, we are saying that cytopathology and respiratory diseases are related and vital in helping specialists identify everything from infections to cancer in the respiratory system by effectively studying collected cellular samples to make the right treatment decision and strategy.
In this article, we will learn how cytopathology and respiratory diseases are connected by discussing applications, techniques, challenges, and limitations related to involved treatment techniques.
Understanding Cytopathology:
Cytopathology is defined as the accurate study of individual cells for disease detection, to indicate any changes in these cells and allow specialists to observe and define the best treatment based on each condition.
Moreover, cytopathology examines cells rather than whole tissue sections, and usually, the tested samples are taken from sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage, and pleural fluid to detect abnormalities associated with respiratory diseases.
This allows cytological analysis to share highly valuable insights for diagnosing diseases where quick and precise analysis is required, with identified cellular patterns to detect infection, cancer, or other conditions, that is why cytopathology and respiratory diseases are this much related.
4 Key Applications of Cytopathology in Respiratory Disease Diagnosis:
Cytopathology and respiratory diseases are closely linked, with cytopathology’s role in examining cellular changes to diagnose a wide range of respiratory conditions.
Thus, understanding the main applications and roles of cytopathology and respiratory diseases for each condition is vital for anyone in the healthcare field:
1. Pneumonia Cytology:
Pneumonia is considered a highly common and serious respiratory condition for all ages, thus, using cytology helps separate between bacterial and viral pneumonia, which is vital in setting the best treatment options and avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use in viral cases.
Often, the pneumonia cytology confirms pneumonia by examining sputum samples to detect pathogens responsible for infection, such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses, it also explores inflammatory cell patterns and other signs of infection that are required to confirm pneumonia.
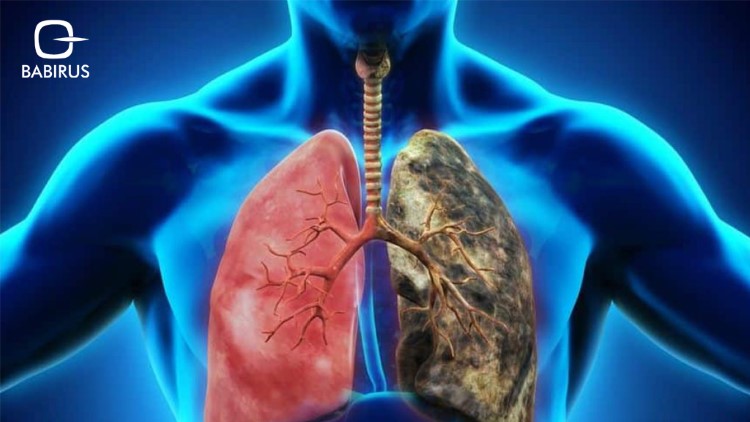
2. Lung Cancer Cytology:
Diagnosing and staging lung cancer totally rely on lung cancer cytology, by collecting cytological samples from sputum, pleural fluid, or bronchial brushings, which provide good clues to malignant cells, and help confirm cancer in patients presenting with respiratory symptoms.
All of that not only helps in the early detection of lung cancer, but also looks for specific cellular abnormalities to define different types of lung cancer, such as small cell or non-small cell carcinoma, and helps in guiding treatment options, including surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
3. Tuberculosis Cytology:
Tuberculosis (TB) is still considered a global health issue, and tuberculosis cytology is one of the most reliable methods for detecting and identifying the disease.
The detecting process usually is done by analyzing sputum samples, where cytologists can identify the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with acid-fast staining to visualize these bacteria, and enable effective diagnosis.
Cytopathology and respiratory diseases play a big role in diagnosing TB in patients with persistent respiratory symptoms, or even those with unclear symptoms, especially in regions where TB is prevalent.
4. Other Respiratory Diseases:
Beyond pneumonia, lung cancer, and tuberculosis, cytopathology and respiratory diseases have many other helpful diagnoses used in many conditions, like chronic bronchitis and interstitial lung diseases.
Additionally, the usage of cytopathology and respiratory disease is highly important for diagnosing and understanding a wider range of respiratory issues, by helping cytologists spot cellular changes more effectively to identify inflammation, long-term infections, or even unusual cells.
Cytopathology Techniques for Respiratory Diseases:
Whether for the respiratory system or any other body part, cytopathology uses various techniques based on the suspected disease and sample type to analyze collected cellular samples and provide cytologists with clear insights to achieve accurate and efficient diagnosis.
· Sputum Cytology:
We can say that sputum cytology is one of the most used cytopathology techniques, particularly, when the patient has a chronic cough or hemoptysis (coughing up blood).
Moreover, this patient-friendly technique involves preparing and analyzing sputum samples for abnormal cells, pathogens, or signs of inflammation for many conditions, including lung cancer, TB, or pneumonia.
· Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL):
BAL is mainly used to get a more comprehensive view of the lower respiratory tract compared to sputum samples, the procedure is done by introducing a saline solution into the lungs and then collected for cellular analysis.
With BAL cytology, cytologists can detect bacteria, fungi, or cancerous cells in BAL samples which is useful for assessing respiratory infections and inflammatory diseases.
· Pleural Fluid Cytology:
Pleural fluid cytology is the used technique to collect and evaluate samples from the pleural space, which is the area between the lungs and chest wall.
This cytological examination can detect malignant cells or infectious agents in the pleural fluid, which is more important to offer insights into disease progression and aid in treatment planning for lung cancer and infections that may spread to the pleural cavity.
· Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Cytology:
FNA cytology is considered a minimally invasive technique that includes extracting cellular material from lung masses or lymph nodes to allow cytologists to examine cells for malignancy, infection, or other abnormalities in the respiratory system.
Furthermore, FNA is especially useful in staging lung cancer, based on the collected cellular samples analyzing results from suspected tumors or nearby lymph nodes.
Main Challenges and Limitations of Cytopathology and Respiratory Diseases:
As we discussed, cytopathology and respiratory diseases are directly attached, however, there are many challenges in the diagnosing process that we cannot ignore:
- Obtaining high-quality samples, as insufficient cellular material can impact the effectiveness of cytological analysis in detecting pathogens or malignancies.
- Getting false negatives is a possibility, if pathogens are not present in the collected sample or if sample handling is suboptimal.
- Having the potential of informational errors, as benign conditions can sometimes mimic malignant features under microscopic examination.
To clarify more, there are certain infections or inflammatory conditions that may cause cellular changes that resemble cancer, leading to diagnostic uncertainty, however, using supplementary techniques, like molecular diagnostics, is required to provide additional information.
Although, cytopathology has its challenges, yet it remains a reliable tool in diagnosing respiratory diseases, once done with skillful understanding and high-quality sample preparation.
To conclude,
Cytopathology and respiratory diseases are two terms that you will hear together, when uncovering respiratory conditions, from simple infections to more serious diseases.
Thus, the development of cytopathology techniques, despite all the challenges, is vital in allowing doctors to detect these diseases early and choose the right treatment to reach the best outcome for the patient.