Understanding Your Complete Blood Count (CBC) Tests
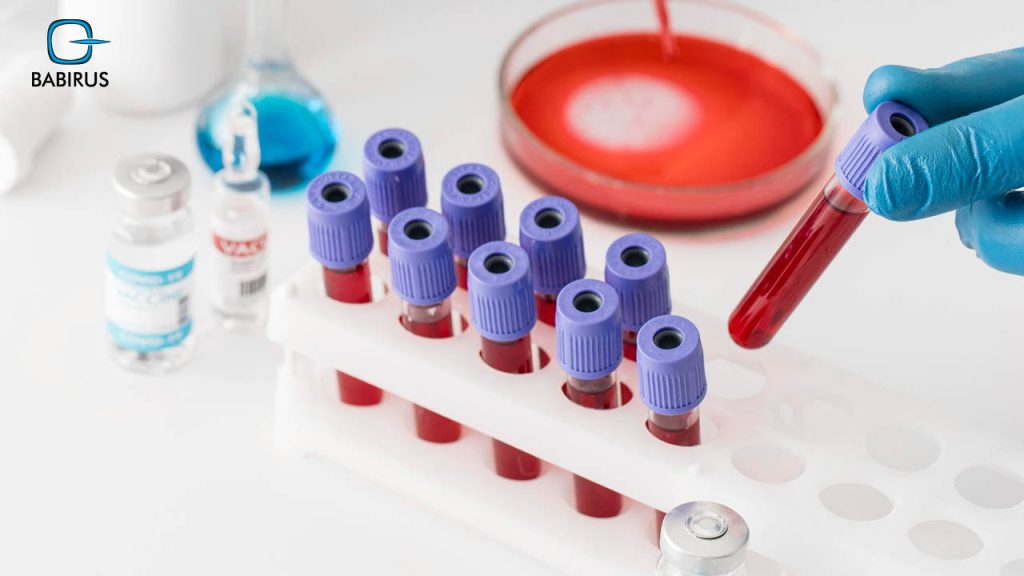
Ordering a complete blood count (CBC) test is considered a first step in the diagnosing and monitoring of many different diseases, as a simple and fast way to get some insights.
Thus, when your doctor orders a complete blood count (CBC) test, it is important to understand that this is usual and does not indicate any serious or dangerous situation, however, you need to know what this test entails and what the results mean for your health.
Today, we will delve into the details of a CBC test, its components, and what the results can indicate about your overall health.
What Is a Complete Blood Count (CBC)?
A CBC test is a basic and routine blood test that offers valuable information about your general health and can help spot a wide range of conditions, including anemia, infection, and leukemia.
Moreover, the CBC test means measuring the following components of your blood to get some helpful insights:
-
Red Blood Cells (RBCs):
The RBCs are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
-
White Blood Cells (WBCs):
The WBCs are important for fighting infections and foreign invaders in the body.
-
Platelets:
Platelets are vital for blood clotting and stopping excessive bleeding.
-
Hemoglobin:
The hemoglobin protein is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and transports carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs.
-
Hematocrit:
The hematocrit measures the percentage of red blood cells in a given volume of blood.
When a CBC Test Is Required?
As we said the CBC test is a regular and easy-to-do blood test that may be performed for various reasons, including:
-
Routine Health Assessment:
A CBC may be done as part of a routine health check-up to evaluate overall health and detect any underlying medical conditions.
-
Monitoring Health Conditions:
People with specific medical conditions, such as anemia, infections, leukemia, or bleeding disorders, may need regular CBC tests to monitor their state and response to treatment.
-
Preoperative Evaluation:
In perfect cases, and before having surgery or some medical procedures, a CBC test must be performed to check the patient’s blood cell counts and general health status to give him/her the best preparation based on his/her condition.
-
Symptoms Evaluation:
CBC tests are most likely the first step in diagnosing, thus, when a person experiences symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, unexplained bruising or bleeding, fever, or other signs of illness, the healthcare provider will order a CBC test to limit potential causes.
-
Medication Monitoring:
Some medications, such as chemotherapy drugs or certain antibiotics, can affect blood cell counts, therefore, regular CBC tests may be necessary to monitor the effects of these medications on the blood.
-
Follow-Up Care:
Patients undergoing treatment for specific conditions may require frequent CBC tests to monitor their progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
What Does a CBC Measure?
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) provides insights into different components of the blood, including:
-
Red blood cells (RBCs) Level:
To identify conditions such as anemia or polycythemia.
-
White blood cells (WBCs) Level:
To recognize infections, inflammation, or other disorders.
-
Hemoglobin Level:
Used to evaluate anemia and monitor patient response to treatment.
-
Hematocrit Level:
This measures the percentage of red blood cells in the blood to diagnose anemia and dehydration conditions.
-
Platelets Level:
To indicate bleeding disorders or clotting disorders platelets are vital for clotting.
-
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) Level:
This measures the average size of red blood cells, it can help in detecting the cause of anemia.

What Diseases Can a CBC Test Detect?
A CBC test clarifies the statistics of the blood components, therefore, it is considered a critical tool in the diagnosing and monitoring of a wide range of medical conditions, such as:
Anemia:
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Vitamin deficiency anemia.
- Anemia of chronic disease.
Infection:
- Bacterial infections.
- Viral infections.
- Fungal infections.
Leukemia and other blood cancers:
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
- Hodgkin lymphoma.
Inflammatory conditions:
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
Blood disorders:
- Sickle cell disease.
- Polycythemia vera.
Read More: What is Multiple Myeloma? Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Why Do Healthcare Providers Order CBC Tests?
The CBC tests help healthcare providers understand the patient’s condition with simple steps, moreover, the use of CBC tests is popular in many diagnosing conditions.
As a diagnostic tool that helps doctors get clear insights and discover abnormalities in the blood that can indicate various medical conditions.
- Healthcare providers order CBCs to monitor the progression of certain health conditions and track the effectiveness of the applied treatment.
- CBC tests are usually ordered as part of routine preventive care, to monitor a patient’s blood cell counts, and detect early signs of certain health problems before symptoms manifest.
- Before surgery, requesting the CBC blood test helps determine a patient’s overall health status and find out if any underlying conditions may pose a risk to the patient during surgery.
- The CBC test helps in medication management for patients who are receiving certain treatments that could reduce or interfere with the production or function of blood cells.
5 Steps to Prepare for the CBC Test:
So, if your family doctor asks you to do a complete blood count test, then there are basic steps that you need to consider when preparing for a CBC test:
1. Consult Your Healthcare Provider:
Before preparing for a CBC test, it is important to ask your healthcare provider for instructions based on your individual health status and any medications you may be taking.
2. Fasting:
In some cases, you will be asked to fast for specific hours before a CBC test, moreover, this involves avoiding food and drink (except water) for a certain period before the test to guarantee real CBC results without any impact on the food and drink.
3. Medication:
Inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking, as some medications can impact the results of a CBC test, and your healthcare provider may recommend you temporarily stop taking certain medications before the test.
4. Hydration:
Staying well-hydrated can make it easier for the healthcare provider to draw blood for the CBC test, moreover, drinking plenty of water in the hours leading up to the test can help ensure that your veins are well-hydrated and more accessible for blood collection.
5. Relaxation:
If you feel anxious about having blood drawn, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation beforehand can help reduce stress and make the experience more comfortable.
Understanding CBC Results and Follow-Up:
It is essential to note that CBC results should be interpreted by a healthcare professional who can take into account your medical history and any symptoms you may be experiencing.
Yet it is still important to understand what each component signifies when you receive the CBC test results:
-
RBC Count:
A low RBC count may indicate anemia, while a high count could suggest dehydration or lung disease.
-
WBC Count:
High WBC counts may indicate infection or inflammation, while low counts could be due to certain medications or bone marrow disorders.
-
Platelet Count:
Abnormal platelet counts may lead to excessive bleeding or clotting disorders.
-
Hemoglobin and Hematocrit Levels:
Low levels may indicate anemia, while high levels could be linked to dehydration or lung disease.
-
MCV, MCH, MCHC:
These values can help identify different types of anemia and provide insights into overall RBC health.
Are There Any Risks Attached to The CBC Test?
While the CBC test is generally considered a simple, safe, and routine procedure, however, as with any other thing, there are some potential risks associated with it:
-
Pain or Discomfort:
The most common risk associated with the CBC test is pain or discomfort when the blood is drawn, still, this is typically a minor issue and resolves quickly after the procedure.
-
Bruising or Bleeding:
Some individuals may experience bruising or bleeding at the site of the blood draw. This can occur if there is difficulty locating a vein or if suitable pressure is not applied to the puncture site after the needle is removed.
-
Infection:
Although rare, there is a small risk of infection at the site where the blood is drawn, however, this risk can be minimized by ensuring that proper sterilization procedures are followed, and the use of totally new tools.
-
Fainting or Lightheadedness:
Some persons may feel faint or lightheaded during or after the blood draw, this can be due to anxiety, low blood sugar, or a vasovagal response to the sight of blood.
-
Hematoma:
In some cases, a hematoma (a collection of blood outside of a blood vessel) may develop at the site of the blood draw, causing localized swelling and discomfort.
-
Nerve Injury:
While extremely rare, there is a small risk of nerve injury at the site where the needle is inserted for the blood draw.
CBC Blood Test in Dubai, Babirus Medical Equipment, your trusted supplier in the UAE.
A complete blood count (CBC) test is a vital diagnostic tool used to evaluate the different components.
Thus, you need to contact Babirus Medical Equipment the trusted supplier of high-quality CBC testing equipment and consumables for manufacturers that meet the latest industry standards.
